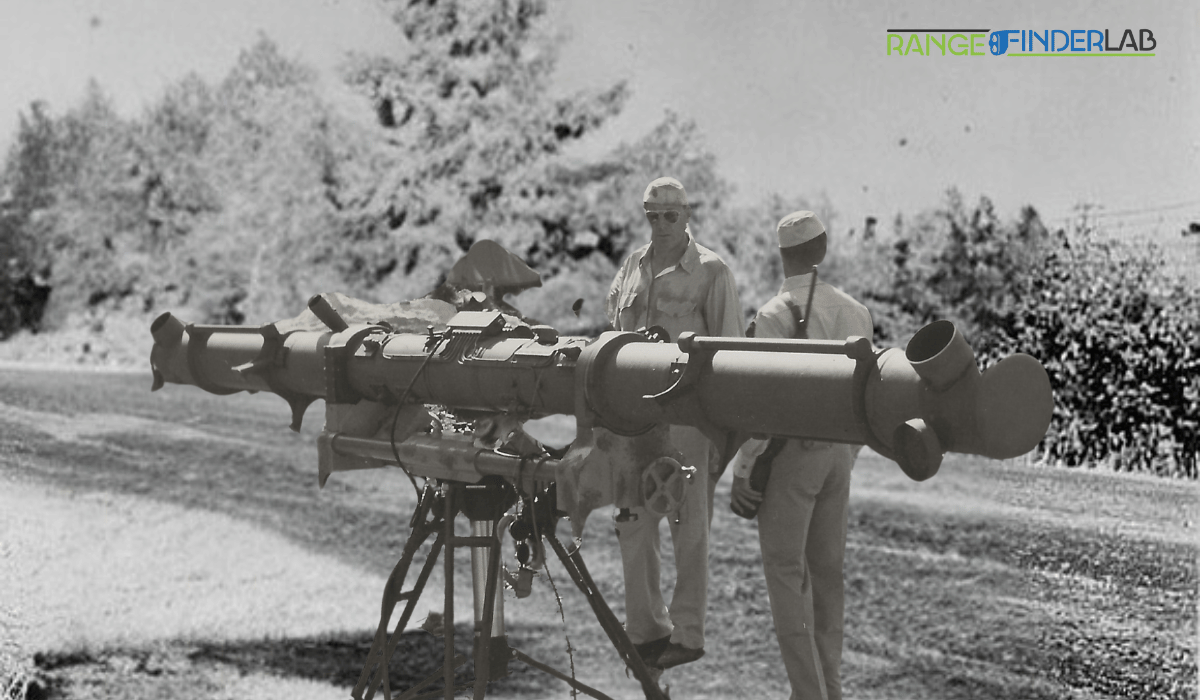
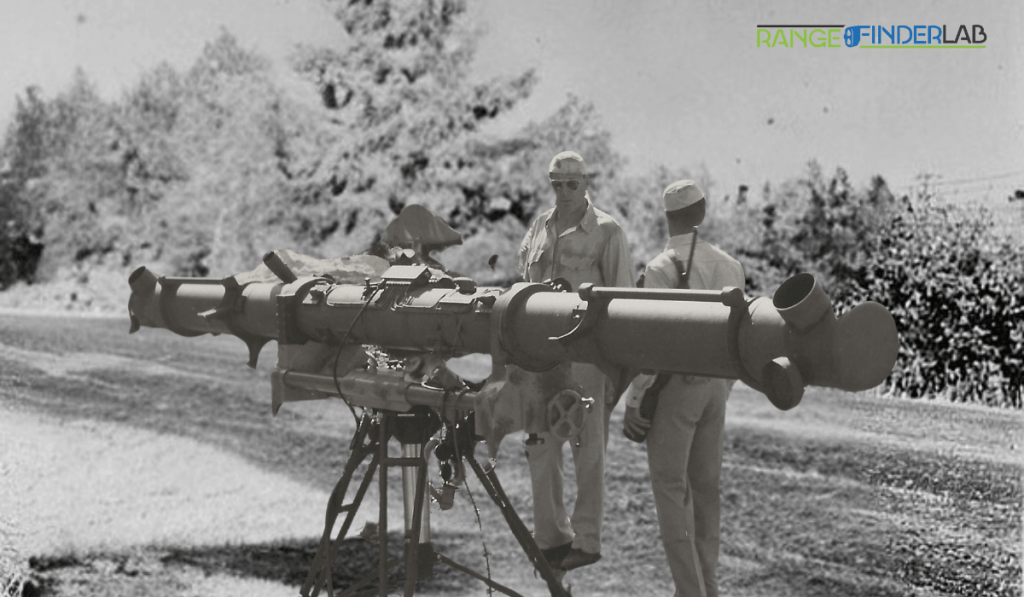
Rangefinders, intricate devices engineered to measure distance, have traversed an extraordinary journey through history, evolving from pivotal military tools to versatile instruments used in various civilian domains. This remarkable evolution paints a vivid picture of technological advancement, where necessity and innovation intertwine to expand the possible boundaries.
The historical significance of rangefinders cannot be overstated. Their inception dates back to the early 20th century, primarily within the military sphere, where precise distance measurement was crucial for effective artillery and naval gunfire. These early rangefinders were predominantly optical, relying on visual cues and manual calculations to estimate distances. Their accuracy and reliability played a critical role in warfare tactics, often determining the outcome of crucial battles.
As technology advanced, so did rangefinders. The advent of laser technology marked a significant leap, introducing a new era of precision and efficiency. This shift was not confined to the military; it spurred a ripple effect, propelling the use of rangefinders into various civilian sectors. Today, they are no longer exclusive to the battlefield. Golfers use them to gauge the distance to the pin, hunters to estimate the range to their prey, photographers to focus their lenses precisely, and surveyors to accurately map out the land.
Join us as we embark on this historical exploration, tracing the rangefinder’s path from its military origins to its widespread civilian applications, and discover how this technology continues to shape and enhance our interaction with the world around us.
Table of contents
The Origins and Military Use of Rangefinders
The story of rangefinders begins with military innovation, where the need for precise distance measurement catalyzed their development and evolution. These devices, initially conceived to enhance the accuracy of artillery and naval gunfire, have played a pivotal role in shaping modern warfare tactics and equipment.
Early History and Development
The genesis of rangefinder technology can be traced back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries. During this period, optical rangefinders, which used visual techniques to estimate distances, were the norm. The most basic form was the coincidence rangefinder, which relied on the user’s ability to align two separate images into one, thereby calculating the distance based on triangulation principles. These early rangefinders were large, often several meters long, and primarily mounted on ships and artillery units.
Another significant development was the stereoscopic rangefinder, which offered a more intuitive approach by mimicking human binocular vision. This technology provided a more natural and accurate way to gauge distance, proving invaluable in World War I and II. The accuracy of these devices was critical in determining the range for gunfire, a factor that often influenced the success or failure of military operations.
Key Advancements and Impact on Military Tactics
The evolution of rangefinder technology was closely intertwined with advancements in optics and, later, electronics. With the advent of infrared and laser technology in the mid-20th century, rangefinders underwent a significant transformation. Using the time-of-flight principle, laser rangefinders, where the time taken for a laser beam to reflect from a target is measured, bring about a new level of precision and ease of use.
These advancements had profound impacts on military tactics and equipment. Accurate distance measurement became crucial for artillery, naval forces, and infantry and air forces. Laser rangefinders enabled faster, more precise targeting, essential in modern combat scenarios where speed and precision are paramount. They became standard equipment in tanks, aircraft, and even handheld devices for ground troops.
Moreover, integrating rangefinders with computerized fire-control systems marked a significant leap in military capability. This combination allowed for real-time data processing, leading to more efficient and effective targeting and a higher probability of mission success.
The military use of rangefinders has been a journey of constant innovation and adaptation. From the bulky optical devices of the early 20th century to the compact, laser-based systems of today, rangefinders have enhanced military effectiveness and laid the groundwork for their diverse applications in civilian life, a testament to the enduring impact of military-driven technological advancements.
Types of Rangefinders and Their Mechanisms
Rangefinders, integral tools for distance measurement, have evolved significantly over the years. They are primarily categorized into two types: optical and laser. Each type has its unique mechanism and historical significance, shaping how we measure distances today.
Optical Rangefinders
Optical rangefinders, the earliest form of this technology, were based on the triangulation principle. They used visual methods to estimate distance. These devices typically consisted of lenses and mirrors arranged to create a split image. The user would align these divided images, and through the principles of trigonometry, the distance to the target could be calculated. While ingenious for its time, this method relied heavily on the user’s skill and the clarity of the visual field.
Historically, the military extensively used optical rangefinders, especially in naval and artillery applications. Their ability to provide reasonably accurate distance measurements without electronic technology was invaluable. For instance, during World War I and II, optical rangefinders were mounted on ships and used for targeting enemy vessels and adjusting artillery fire.
Laser Rangefinders
Laser rangefinders marked a revolutionary advancement in this field. They operate on the principle of time-of-flight. In this method, the rangefinder emits a laser beam towards the target, which reflects to the device. The time taken for the round trip of the laser beam is measured, and using the speed of light, the distance to the target is calculated. This method brought unprecedented accuracy and speed in distance measurement.
The first substantial use of laser rangefinders was also in the military. They provided a significant advantage due to their accuracy, even over long distances, and were less affected by environmental factors than optical rangefinders. Laser rangefinders are widely used in various fields, including golf, hunting, forestry, and surveying. Modern laser rangefinders are compact, highly accurate, and user-friendly, starkly contrasting their bulkier, more complex predecessors.
The evolution from optical to laser rangefinders represents a technological leap from manual, visually dependent devices to highly accurate electronic instruments. This transition enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of distance measurement and broadened the application spectrum of rangefinders beyond military use, embedding them into the fabric of various civilian activities.
Transition to Civilian Applications
The journey of rangefinders from military-exclusive tools to essential gadgets for civilian use is a fascinating aspect of their evolution. This transition was driven by technological advancements and a growing recognition of their utility in various non-military domains.
Post-Military Adoption
After World War II, the technological boom and the shift toward consumerism paved the way for rangefinders to enter the civilian market. Initially, these devices were expensive and somewhat cumbersome, limiting their use to specific professional fields. However, as technology advanced, rangefinders became more affordable, compact, and user-friendly, leading to a surge in their civilian applications.
Civilian Uses of Rangefinders
- Hunting: Rangefinders revolutionized hunting by allowing hunters to accurately measure the distance to their target, significantly increasing the chances of a successful and ethical shot. Hunters often use rangefinders with specialized features like angle compensation, which accounts for the terrain’s incline or decline.
- Golfing: In golf, rangefinders assist players in gauging the distance to the hole or specific points on the course. This information is crucial for selecting the right club and planning the shot. Golf rangefinders often include features like slope measurements and GPS integration.
- Photography: Photographers, especially in wildlife and sports genres, use rangefinders to determine the distance to their subject for focusing and framing purposes. Rangefinders in cameras have evolved significantly, with modern digital cameras integrating sophisticated rangefinding technologies.
- Surveying: Rangefinders have become indispensable in surveying and construction. They provide quick and accurate measurements of distances, heights, and angles, which are crucial for mapping, planning, and executing construction projects.
The transition of rangefinders to civilian use not only democratized this technology but also sparked innovation, leading to the development of specialized rangefinders catering to the needs of different activities. From being a strategic military instrument to becoming a tool enhancing efficiency and precision in various civilian sectors, rangefinders have undoubtedly made a significant mark beyond their original scope of use.
Technological Evolution and Modern Innovations
The technological trajectory of rangefinders is marked by continuous innovation and adaptation, resulting in increasingly sophisticated, user-friendly, and versatile devices. This section delves into the significant technical milestones and the cutting-edge innovations shaping the current rangefinder landscape.
Major Technological Advances
- Miniaturization: One of the most significant advancements has been the miniaturization of rangefinder components. This has led to more compact, lightweight, easily portable devices, a stark contrast to the bulky and cumbersome early models.
- Laser Technology: The introduction of laser rangefinders was a game-changer. Unlike optical rangefinders that rely on manual calculations, laser rangefinders use a laser beam to measure distance with remarkable accuracy and speed. This technology has been refined over the years, enhancing precision and range.
- Digital Integration: The integration of digital technology has transformed rangefinders into multi-functional devices. Modern rangefinders feature digital displays, GPS functionality, data storage, and even connectivity with smartphones and other digital devices for enhanced functionality.
Current Innovations and Trends
- Smart Rangefinders: The latest rangefinders have innovative technology, including Bluetooth connectivity and app integration. This allows users to sync their rangefinder with mobile apps for advanced features like ballistic calculations, weather conditions, and GPS mapping.
- Multi-Purpose Sensors: Newer models are equipped with various sensors that measure not just distance but also factors like wind speed, temperature, and humidity, providing a comprehensive set of data for precise calculations in activities like hunting and golfing.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: Emerging trends include incorporating AR technology, where the rangefinder can overlay data onto a real-time view of the target area, enhancing user experience and accuracy.
- Environmentally Adaptive Technologies: Rangefinders are now designed to adapt to environmental conditions, such as fog, rain, and extreme sunlight, ensuring reliable performance in diverse scenarios.
- Sustainable and Durable Designs: With a growing emphasis on sustainability, newer rangefinders are being developed with eco-friendly materials and designed for enhanced durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
These technological evolutions and modern innovations signify a bright future for rangefinder technology, with potential applications expanding into new domains and offering unprecedented levels of precision, convenience, and versatility for users.
Expert Insight: Personal Opinion and Feedback
As someone deeply immersed in the world of rangefinders, I’ve observed their evolution with both admiration and awe. This journey from military essentials to ubiquitous civilian tools is not just a tale of technological progress; it’s a narrative about adaptability and the endless quest for precision and convenience.
My Unique Perspective on Rangefinder Technology
In my view, rangefinder technology has always been a fascinating intersection of necessity and innovation. In the military context, the precision of a rangefinder could mean the difference between success and failure, often under incredibly challenging conditions. The demand for accuracy and reliability in high-stakes situations drove the initial technological leaps in rangefinder development. It was this foundation that set the stage for future innovations.
The transition of rangefinders into civilian life is equally compelling. It’s a testament to how military technologies can find new life and purpose in peacetime. The civilian adoption wasn’t just about making rangefinders more compact or user-friendly; it was about reimagining their applications. In golf, hunting, photography, and surveying, rangefinders have become precision tools, enhancing the experience and outcomes in each field.
Reflection on the Significance of Rangefinders
Reflecting on the significance of rangefinders, I believe their value lies in their ability to bridge the gap between human limitation and the need for accuracy. In the military, rangefinders have saved lives by enabling precise targeting. In civilian uses, they bring precision to recreational and professional activities that would be impossible to achieve otherwise.
The evolution of rangefinders is ongoing. The future looks bright with advancements in laser technology, integration with artificial intelligence, and the continuous miniaturization of devices. I envision more accurate, faster, and more integrated rangefinders with our other devices and daily lives.
In conclusion, the story of rangefinders is one of remarkable progress and transformation. From their early military days to their widespread use today, rangefinders have proved to be more than just tools – they are a testament to human ingenuity and our relentless pursuit of perfection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the history of rangefinders?
- Rangefinders date back to the early 20th century, initially developed for military use in artillery and naval operations. Early models were primarily optical, using triangulation to estimate distances. The introduction of laser technology in the latter half of the century revolutionized rangefinders, leading to their widespread use in both military and civilian applications.
2. Does the military still use rangefinders?
- Yes, the military continues to use rangefinders and incredibly advanced laser models. They are essential for precision targeting in various military operations, including artillery fire control and surveillance.
3. What are the main types of rangefinders?
- The two primary types of rangefinders are optical and laser. Optical rangefinders estimate distance based on visual triangulation, while laser rangefinders use the time-of-flight of a laser beam to calculate distance.
4. How does an old optical rangefinder work?
- Old optical rangefinders work on the principle of triangulation. They have two lenses at opposite ends of a baseline. The user aligns two images of the target seen through these lenses, and the convergence angle is used to calculate the distance based on trigonometry.
5. What is the average range of a modern laser rangefinder?
- The range of modern laser rangefinders can vary widely depending on the model and intended use. Typically, they can measure distances from as close as 10 yards to as far as 1,500 yards or more.
6. Are there waterproof rangefinders for marine use?
- Yes, there are waterproof rangefinders explicitly designed for marine use. These are built to withstand harsh marine environments and often have additional features like buoyancy and marine-focused optics.
7. Can rangefinders measure speed as well as distance?
- Some advanced rangefinders, particularly those designed for military or law enforcement use, can measure speed in addition to distance, utilizing Doppler radar technology.
8. How accurate are rangefinders in measuring long distances?
- Modern laser rangefinders are highly accurate, even over long distances. They can typically provide measurements within a few yards of accuracy at ranges of 1,000 yards or more.
9. Are rangefinders easy to use for beginners?
- Many modern rangefinders are designed with ease of use in mind, making them accessible for beginners. Features like automatic target acquisition and transparent displays contribute to their user-friendliness.
Conclusion
The journey of rangefinders from their early military origins to their widespread civilian use today is a fascinating story of technological evolution and innovation. Initially developed for precise targeting in military operations, rangefinders have adapted and evolved, finding a place in various civilian fields such as hunting, golfing, photography, and surveying. This transition underscores not only the versatility of the technology but also its continuous improvement and adaptation to different needs.
Key takeaways from our exploration include understanding the fundamental differences between optical and laser rangefinders and recognizing the significant advancements that have been made in terms of accuracy, portability, and functionality. The modern rangefinder, with its sophisticated laser technology and advanced features, is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of precision.
As we reflect on the historical significance and the current applications of rangefinders, it’s clear that this technology has not only shaped various professional fields but has also become an integral tool for enthusiasts and hobbyists. The future of rangefinders looks promising, with ongoing innovations to enhance accuracy, range, and user experience.
I encourage readers to delve deeper into the world of rangefinders to appreciate their technical prowess and the rich history behind this remarkable technology. Whether you are a professional needing precise measurements, an avid golfer, a wildlife enthusiast, or someone interested in the mechanics of optical instruments, rangefinders present a fascinating and valuable tool, continually evolving to meet the demands of the modern world.








